First of all, we need to understand some terms because different people use different terms to understand the word demand.
Desire: Desire cannot be defined simply, because it can be different for different living things. For example, the one who has nothing to eat will desire to get food, similarly, the one who does not have a vehicle will desire to get a vehicle.
Needs: It is necessary to have essential elements to survive because survival is not possible without essential elements. These essential elements are called needs. Like food, water, etc. are essential elements for survival.
Wants: Wants do not imply essential elements because it is possible to survive even without them. This is necessary only for a better life. Like, better infrastructure, etc.
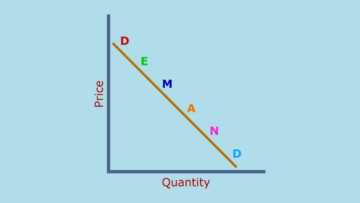
Table of Contents
What is Demand?
Meaning of Demand
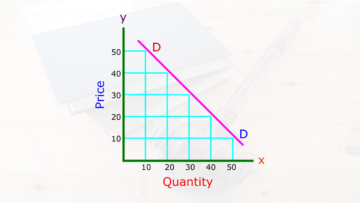
Demand means willingness to buy, ability to buy and ready to buy at a specific price, time and place. Demand is called only when all the elements of demand are fulfilled. Demand completely depends on the market conditions because market conditions affect the demand. Like, buyer’s interest, buyer’s ability, population, government policies, etc.
If someone has interest in buying goods and services but does not have the ability to buy, then it will not be called demand, similarly, if someone has the ability to buy, but does not have the interest to buy, then it will not be called demand.
Definition of Demand
According to Benham – “The demand for anything at a given price is the amount of it, which will be bought per unit of time that price.”
According to Hibdon – “Demand means the various quantities of a good that would be purchased per time period at different prices in a given market.”
According to Professor Meyers – “The demand for goods is schedule of the amounts that buyers would be willing to purchase at all possible prices at any one instant of time.”
According to Ferguson – “Demand refers to the quantities of a commodity that the consumers are able and willing to buy at each possible price during a given period of time, other things being equal.”
Elements of Demand
Following are the elements of demand:
- Willingness to buy.
- Ability to buy (Purchasing power).
- Ready to buy.
- Specific price, time, place etc.
Determinants of Demand
Following are the determinants of demand:
1. Price of a commodity:
The price of a commodity directly affects the demand because if the price of a commodity decrease then the demand for that commodity increase, similarly if the price of a commodity increase then the demand for that commodity decrease.
2. Population:
Population also directly affects the demand because if the population is high then the demand for goods and services will also be high, similarly if the population is low then the demand for goods and services will also be low.
3. Price of related commodity:
It is divided into two parts.
- Substitute goods.
- Complementary goods.
- Substitute goods: Those goods which are used in place of each other are called substitute goods. Like, tea and coffee, Coca-Cola and Pepsi, etc. If the price of any one of these goods increases, the demand for the other good will automatically increase.
- Complementary goods: Those goods which directly affect the demand of each other are called complementary goods. Like, car and diesel pen and ink etc. If the price of one commodity increases, the demand for the other commodity automatically decreases.
4. Festivals:
Festivals also impact demand, because demand for related goods increases during the festival season. For example, the demand for firecrackers and sweets increases during Diwali.
5. Income of the consumer:
If the consumer’s income is high, he demands more goods and services, similarly if the consumer’s income is low, he demands less goods and services. Therefore, consumer’s income also affects demand.
6. Weather:
Weather also affects demand. e.g., the demand for hot goods is more in winter, similarly the demand for cold goods is more in summer.
7. Expectations:
If the price of goods is likely to increase in the future, consumers will demand more goods in the present. Similarly, if the price of a good is likely to decrease in the future, consumers will reduce their demand for that good in the present so that they can buy that good when the price decrease in the future. This is why expectations also affect demand.
Read Also:
FAQ/Q&A
Q1. What is Demand?
Ans: Demand means willingness to buy, ability to buy and ready to buy at a specific price, time and place.
Q2. Does population affect demand?
Ans: Yes
Q3. Is purchasing power important for demand?
Ans: Yes
Q4. Write the elements of demand.
Ans: Following are the elements of demand.
1. Willingness to buy.
2. Ability to buy (Purchasing power)
3. Ready to buy.
4. Specific price, time, place etc.
Q5. Write the determinants of demand.
Ans: Following are the determinants of demand.
1. Price of a commodity
2. Population
3. Price of related commodity
4. Festivals
5. Income of the consumer
6. Weather
7. Expectation